Residential Solar Power Plants

Residential solar power systems are designed for individual homes. They typically consist of solar panels installed on rooftops or in yards, converting sunlight into electricity for household use. Benefits include reduced energy bills, increased property value, and environmental sustainability. Homeowners can often take advantage of tax incentives and rebates, making the initial investment more manageable.
On-Grid Residential Solar Plants

Description: These systems are connected to the local electricity grid, allowing homeowners to use solar energy directly and sell excess energy back to the grid through net metering.
Installation: Involves the placement of solar panels on rooftops or in yards, an inverter to convert DC electricity to AC, and a connection to the grid. Professional installation is crucial for optimal energy efficiency and compliance with local regulations.
Service: Regular monitoring and support ensure the system operates at peak performance. This may include remote monitoring systems that alert homeowners to any issues.
Maintenance: Requires periodic cleaning of panels, inspection of electrical components, and performance checks. Typically, maintenance is minimal, but a professional service is recommended annually.
Insurance: Homeowners should consider solar plant insurance to cover potential damages from weather events, theft, or liability issues, ensuring financial protection for their investment.
Off-Grid Residential Solar Plants
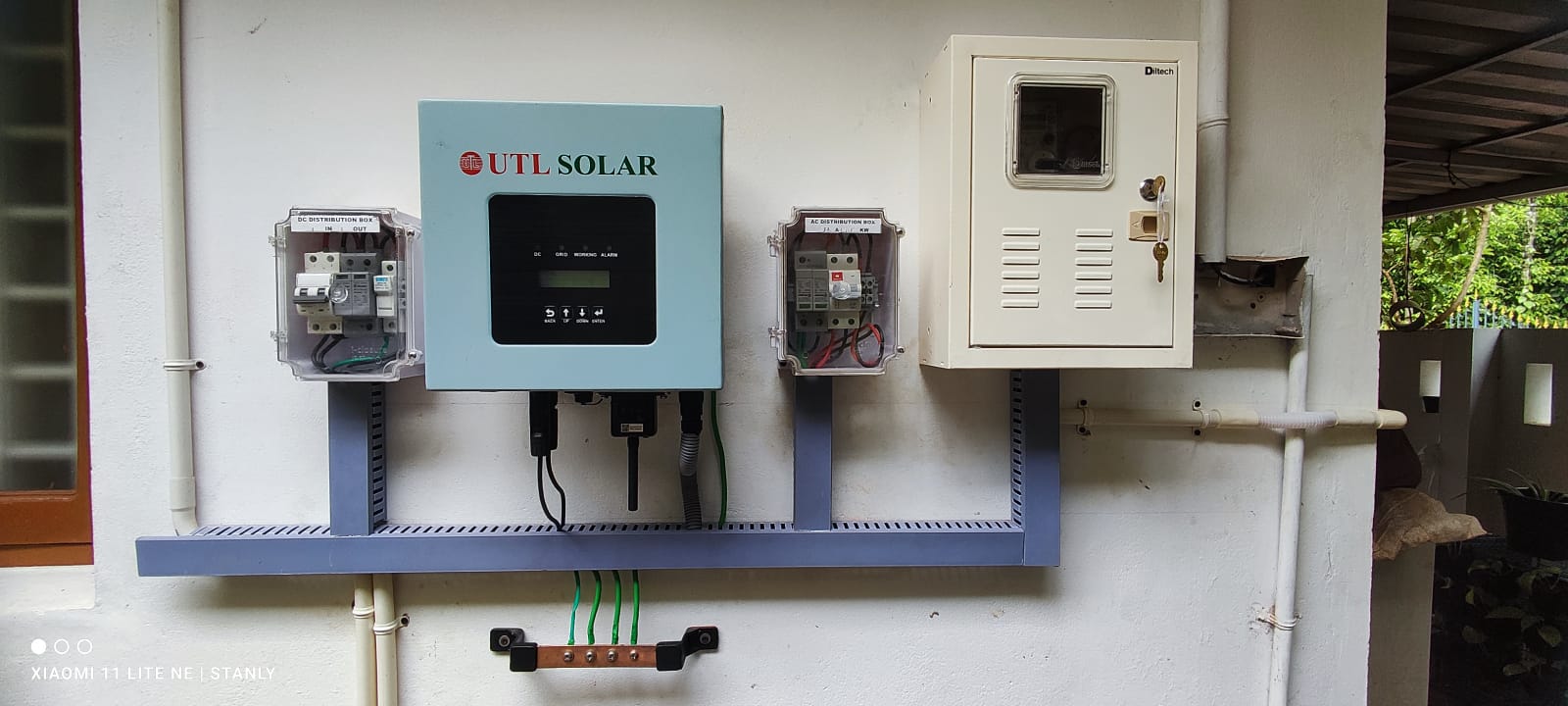
Description: Off-grid systems operate independently of the electricity grid and include battery storage to provide power during non-sunny periods. They are ideal for remote locations or for those seeking complete energy independence.
Installation: This involves solar panels, a battery bank, charge controllers, and an inverter. Proper sizing of the battery bank is essential to meet energy needs during low solar production periods.
Service: Ongoing service includes monitoring battery health and system performance, ensuring the batteries are charged and functioning optimally.
Maintenance: Regular checks on battery levels, panel cleaning, and system inspections are vital. Off-grid systems may require more maintenance compared to on-grid systems due to the complexity of battery management.
Insurance: Similar to on-grid systems, insurance is important to protect against potential damages and liabilities, especially considering the higher investment in battery technology.
Hybrid Residential Solar Plants

Description: Hybrid systems combine both on-grid and off-grid capabilities, allowing homeowners to draw power from the grid or utilize stored energy in batteries. This flexibility enhances reliability, especially during power outages.
Installation: Involves more complex setups, including solar panels, inverters (possibly hybrid inverters), and battery storage systems. Professional installation is crucial for integrating all components effectively.
Service: Continuous monitoring is necessary to manage energy flows between the grid and battery storage, ensuring efficiency and responsiveness to energy needs.
Maintenance: Regular maintenance includes checks on both the solar and battery systems, ensuring they are functioning correctly. Monitoring software can help identify issues early.
Insurance: Insurance for hybrid systems should cover both solar components and battery systems, protecting against a range of risks.
Commercial Solar Power Plants
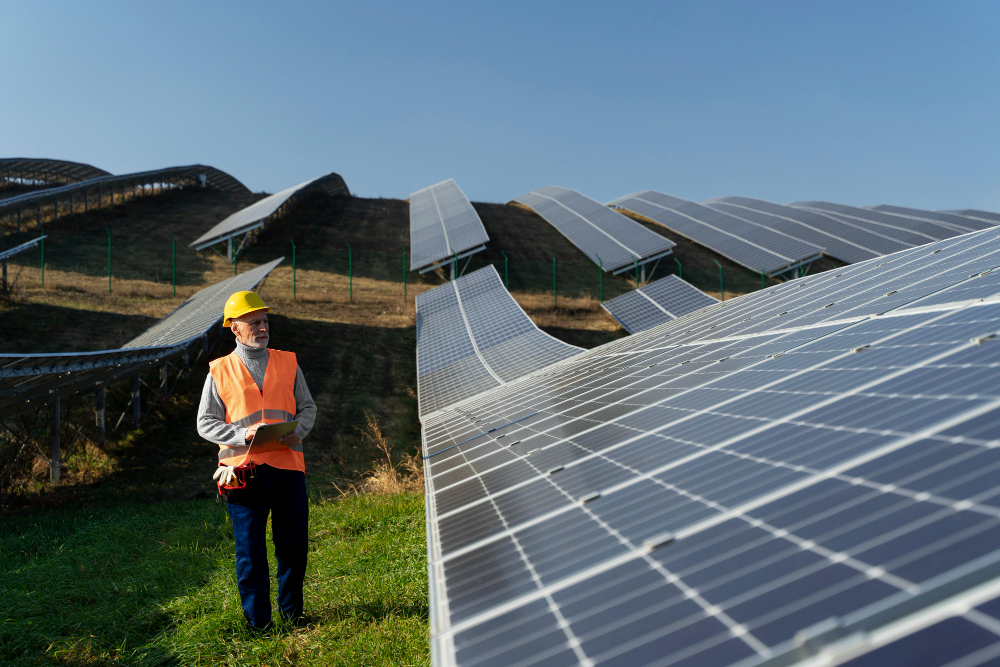

Commercial solar power systems are larger installations meant for businesses, schools, or other organizations. They can be installed on rooftops, parking lots, or as standalone ground-mounted systems. These plants generate significant amounts of electricity, helping businesses reduce operational costs and carbon footprints. Many commercial entities also benefit from renewable energy credits and government incentives, making solar a financially attractive option.
On-Grid Commercial Solar Plants
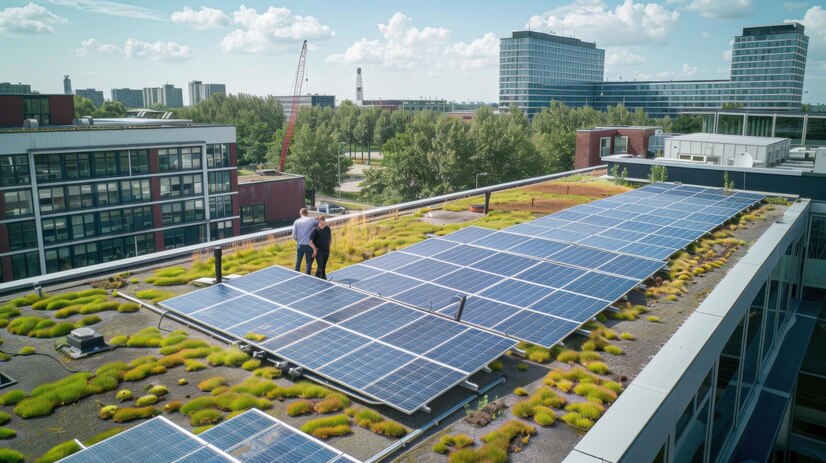

Description: These larger installations are designed for businesses, schools, and other organizations, connected to the public electricity grid to optimize energy use and reduce costs.
Installation: Involves a detailed assessment of energy needs, followed by the installation of solar panels, inverters, and a connection to the grid. Given the scale, professional installation is essential to meet regulatory requirements and maximize efficiency.
Service: Commercial systems often include comprehensive service agreements, offering regular monitoring, performance assessments, and support to ensure uninterrupted energy production.
Maintenance: Maintenance tasks include regular cleaning, inspections, and performance checks. Commercial systems may require more frequent service due to higher energy demands and operational complexity.
Insurance: Businesses should invest in solar plant insurance to cover equipment damage, liability, and business interruption, safeguarding their investment.
Off-Grid Commercial Solar Plants

Description: Ideal for businesses in remote locations without grid access, these systems generate and store their own energy.
Installation: The setup involves solar panels, battery storage, and inverters, with careful planning to ensure the system meets the energy demands of the business.
Service: Service agreements often include performance monitoring and battery health checks, ensuring the system operates effectively.
Maintenance: Off-grid commercial systems require regular maintenance, especially for battery systems, including monitoring battery levels and ensuring solar panels are clean and functional.
Insurance: Insurance is crucial to protect against damages, operational disruptions, and liability, ensuring the business can continue to function smoothly.
Hybrid Commercial Solar Plants

Description: These systems provide flexibility by combining on-grid and off-grid functionalities, enabling businesses to use grid power or stored energy as needed.
Installation: The installation process is complex, requiring a detailed analysis of energy usage patterns and careful integration of solar panels, inverters, and battery systems.
Service: Hybrid systems typically come with robust service agreements, offering ongoing monitoring and support to manage energy sources effectively.
Maintenance: Regular checks are needed for both solar panels and battery systems, ensuring reliability and efficiency. Maintenance may involve both preventative and corrective measures.
Insurance: Comprehensive insurance coverage is essential to protect against various risks, including equipment damage and business interruptions.
